This article is part of a series on COVID-19 focusing on how the outbreak is affecting industries.
Three months after the first outbreak of Coronavirus (COVID-19) in China, it is now known that older age and underlying health conditions are risk factors when a person is infected. While ageing populations in Japan, Italy and Greece are at greater risk, emerging and developing countries in the Middle East and Eastern Europe could be vulnerable due to prevalent health risks among their populations.
The situation is further compounded by urbanisation, which has swelled cities into densely packed areas, making them effective breeding grounds for the COVID-19 virus. Indeed, social distancing has been touted as an effective way to avoid rapid transmission of the virus, but it can be challenging to implement in today’s highly urbanised, mobile and densely populated world.
Japan sees the world’s highest death rate from diseases of the respiratory system
With more than one-fifth of their populations aged 65+ in 2019, countries like Japan, Italy and Greece are at most risk from the COVID-19 outbreak. Partly due to its ageing population, Japan already has the highest death rate from diseases of the respiratory system in the world, though the country has a very good functioning healthcare system.
In comparison, Italy’s death rate from respiratory diseases is lower than in Japan, Greece and Portugal. However, a relatively low number of hospital beds is undermining Italy’s ability to cope with a rapid COVID-19 outbreak.
Top 10 Countries with the Highest Shares of Population Aged 65+ with Corresponding Death Rates from Respiratory Diseases 2019
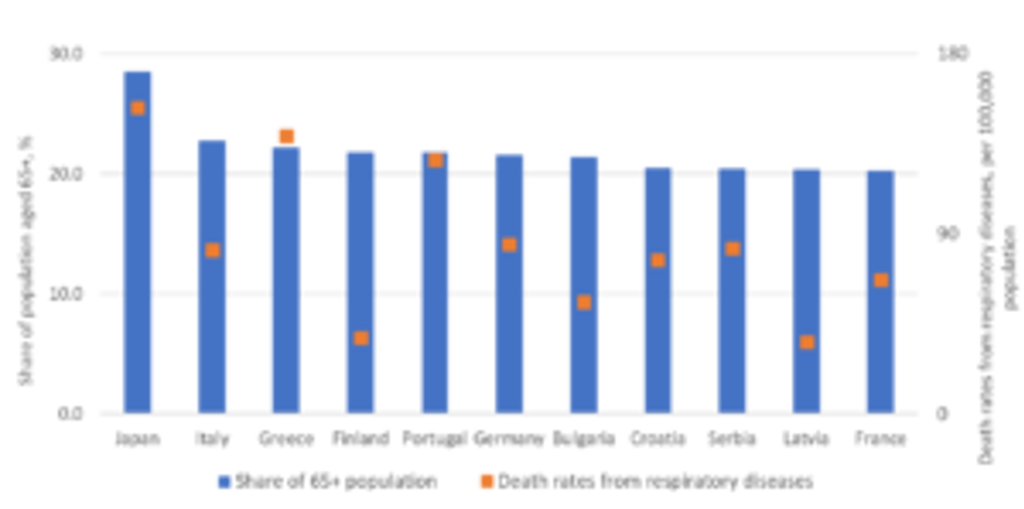
Source: Euromonitor International from national statistics/UN/WHO
Densely populated cities such as London and Barcelona will be tested
With Europe now at the epicentre of the COVID-19 outbreak, urban areas will face a test in stemming the spread of the virus. Population density, which measures the number of people living per sq km of land, can be a significant measure of how fast a virus will be transmitted since densely populated cities can become active breeding grounds for infectious diseases.
Cities such as London and Barcelona are now facing a great challenge, with population densities averaging around 1,900 people per sq km. Social distancing can be complex in densely populated cities where the large majority live in apartments. Moreover, the high degree of public transport usage across these cities further amplifies the risk of the virus spreading.
The COVID-19 pandemic also poses a great threat to ageing cities in Europe. This is especially a problem in Italian and Spanish cities, which contain some of the oldest populations in the region; for example, in Milan and Bilbao, 23% of the population is over the age of 65 years – relatively high figures compared to other European cities, such as Stockholm (16%) and Paris (15%).
Smaller cities, in this respect, face a great danger as their populations tend to have an even higher share of the elderly (given that younger segments of the population typically move to larger cities in search of employment and education opportunities). For instance, in the Italian coastal city of Genoa, around 29% of the population was over the age of 65 years in 2019. This increases the vulnerability of healthcare systems in smaller cities and ultimately could lead to a severe shortage of hospital bed space, should viral infections spiral out of control.
Population Density and Share of Older Population in Major European Cities 2019
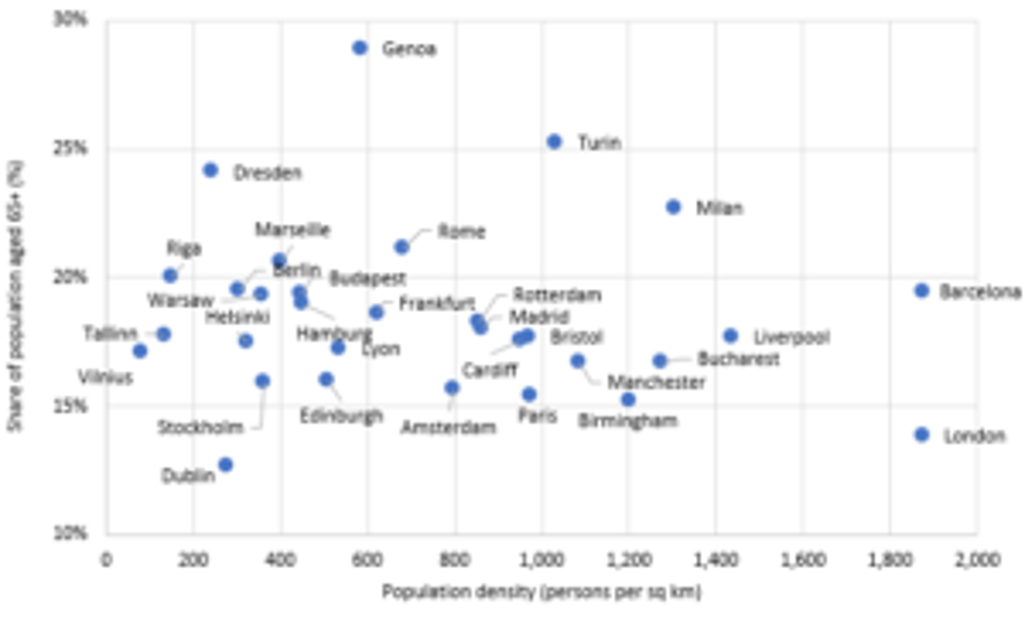
Source: Euromonitor International from national statistics/UN
Other health conditions make some Middle Eastern and Eastern European populations vulnerable
In China, it was reported that people with diabetes had much higher rates of serious complications and death when they contracted COVID-19 than people without diabetes. Though declining, the Middle East region continues to have among the highest diabetes prevalence in the world. Due to changing diets and an overall lack of physical activity, 18% of 20-79-year-olds in Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates and Egypt had diabetes in 2019.
Countries with the Highest Diabetes Prevalence Rate 2019
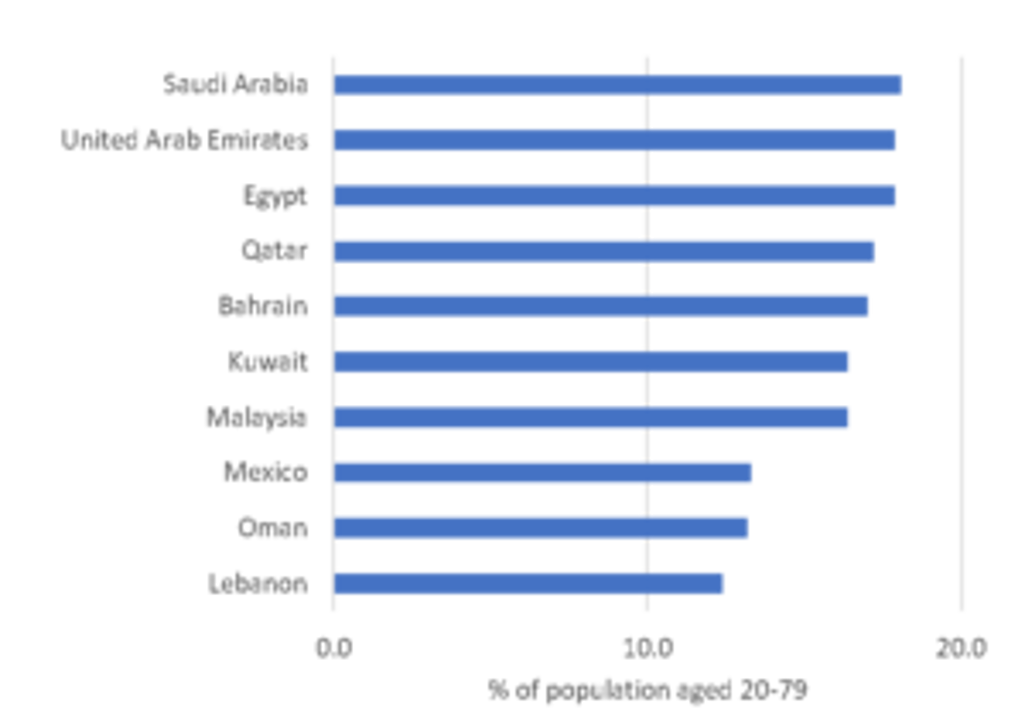
Source: Euromonitor International from Eurostat/OECD/WHO/national statistics/International Diabetes Federation. Note: Ranking out of 103 countries
High blood pressure is also a risk factor in the severity of COVID-19, according to a study published in The Lancet – a well-known medical journal – in March 2020. Looking at hypertension indicator, Eastern European populations have significantly higher prevalence rates compared to other regions. This can be due to genetic factors while eating and drinking habits also play an important role. With almost 30% of over 18-year-olds having high blood pressure, the populations of Estonia, Latvia, Ukraine and Lithuania are at greater risk from a COVID-19 outbreak.
Hypertension Prevalence by Region 2010-2019
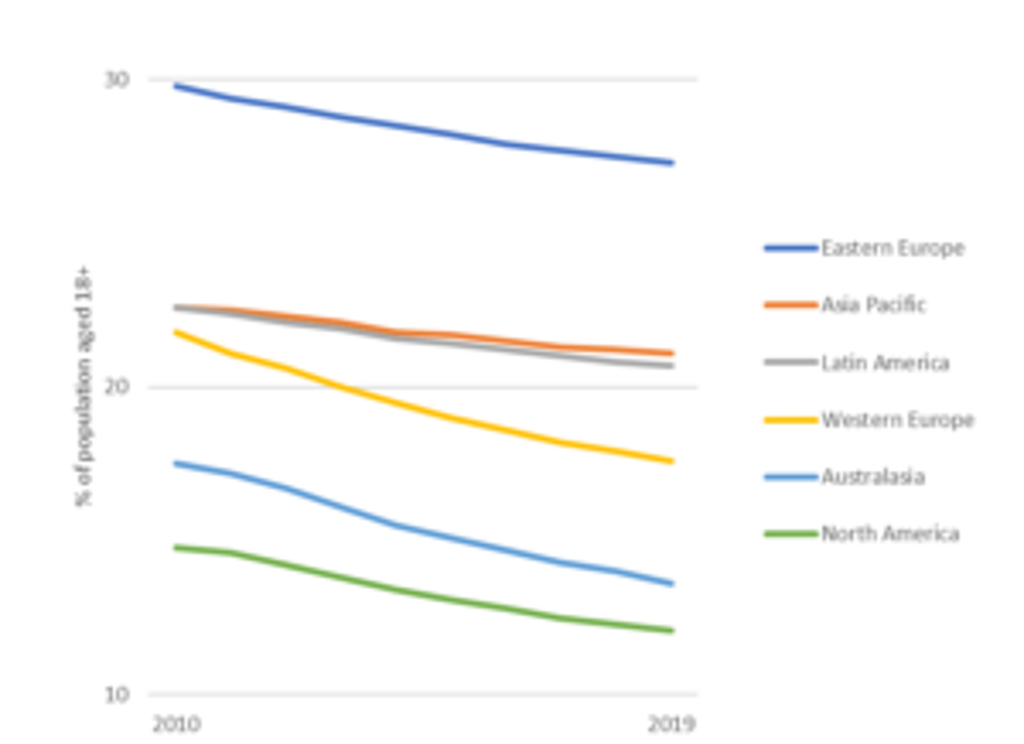
Source: Euromonitor International from WHO. Note: (1) High blood pressure refers to the percentage of the population aged 18+ with systolic blood pressure = 140 or diastolic blood pressure = 90. (2) Data for the Middle East & Africa region is unavailable
Infrastructure and health likely to gain in importance beyond the outbreak
The pandemic has underlined the importance of public health among governments, and an awareness of the fact that we live in an increasingly ageing population that often comes with many challenges, prompting healthcare systems and infrastructure to adjust. Countries and cities may now need to increase the number of hospital beds to coincide with the rise in the average age of their populations.
On the other hand, more consumers will likely pursue healthier lifestyles and opt for self-prevention in the aftermath of the pandemic. According to Euromonitor International’s Health and Nutrition Survey in 2019, physical activity and nutrition already formed the centre of consumers’ preventative health actions. Doing exercise and sport was selected by 63% of all global respondents as their approach to preventing health problems. As such, products and services that support consumers achieve their health goals will gain growing popularity in the future.
