Retailers in most countries have not faced an economic fallout of this magnitude since the global financial crisis of 2007-2009. The overall retailing industry declined 3% in 2009 in nominal value terms, only one of two declines over the last 15 years, but quickly rebounded in 2010 with 6% growth. The Coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic is expected to trigger a global recession, but the cause and impact will be different.
Following the global financial crisis, there were signs of recovery by early 2010, although unemployment and debt levels remained high in some markets. Emerging economies, such as China, Brazil and India, were less impacted and recovered more quickly. Most developed markets, notably Australia, France, Germany, Italy, Spain and the UK, registered negative sales growth across fast-moving consumer goods in 2009. The US, where the recession started, began to recover in late 2009. By then, however, the global economic downturn already had a profound effect on consumer spending habits.
Conspicuous consumption declined as demand for value rose
In the developed world, job losses, economic uncertainty and public austerity measures dampened consumer confidence. Value for money became a key driver for most shoppers, with quality and price emerging as motivations when making purchasing decisions. Lavish spending took a back seat. Consumers sought special offers and used coupons more frequently. They also eschewed upscale supermarkets in favor of discounters and online retailers, which sold products at cost-effective prices.
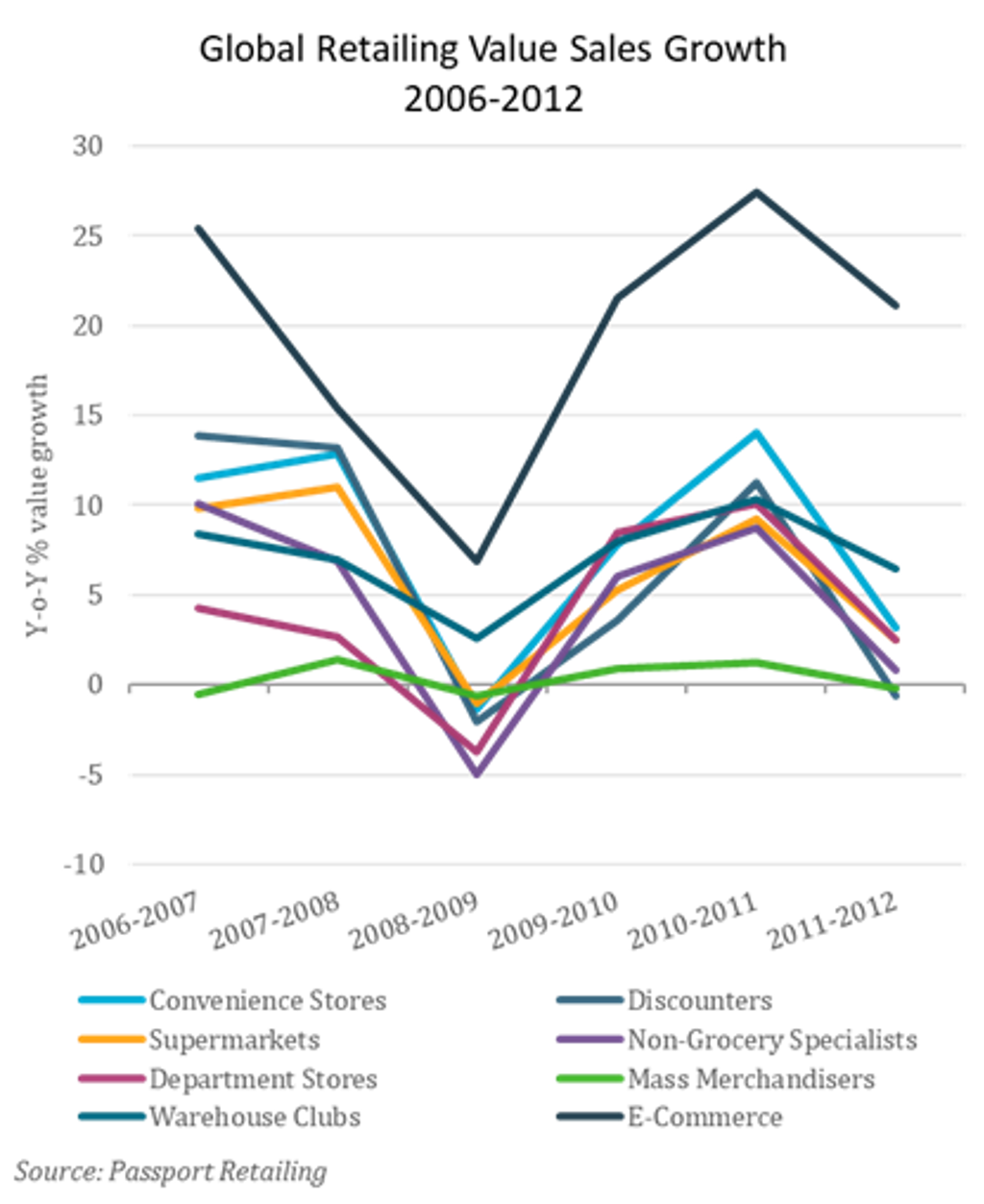
The change in consumer sentiment followed a long period of decadence. Conspicuous consumption had given way to frugality, whereby consumers took a toned-down approach to everything. Former necessities became luxuries, and indulgence felt more shameful than deserved. Buying designer labels at discounted prices became popular, giving consumers a sense of value. Although conditions improved, consumers became accustomed to seeking value and continued to shop at discounters and purchase private label products.
Lessons from South Korea’s MERS crisis
In 2012, the first case of Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS) was identified in Saudi Arabia. With 186 people infected, including 38 deaths, the MERS outbreak in South Korea was the largest outside of Saudi Arabia. During the outbreak in 2015, South Koreans avoided crowds for fear of infection. As such, places that attract large crowds, including shopping centers, theme parks, sports venues and subways, reported a sharp drop in foot traffic.
The outbreak slashed South Korea’s annual economic growth by 0.3 percentage points. Slowing global demand for its goods, combined with sluggish consumer demand at home, hit the country’s export-led economy hard. Store-based retailing in South Korea experienced a sharp decline in 2015, but grocers and off-price retailers were impacted the least by these behavioral shifts. A majority of the store-based formats most impacted by the outbreak saw sales return to pre-MERS levels by 2017.
South Koreans turned to e-commerce during the MERS crisis
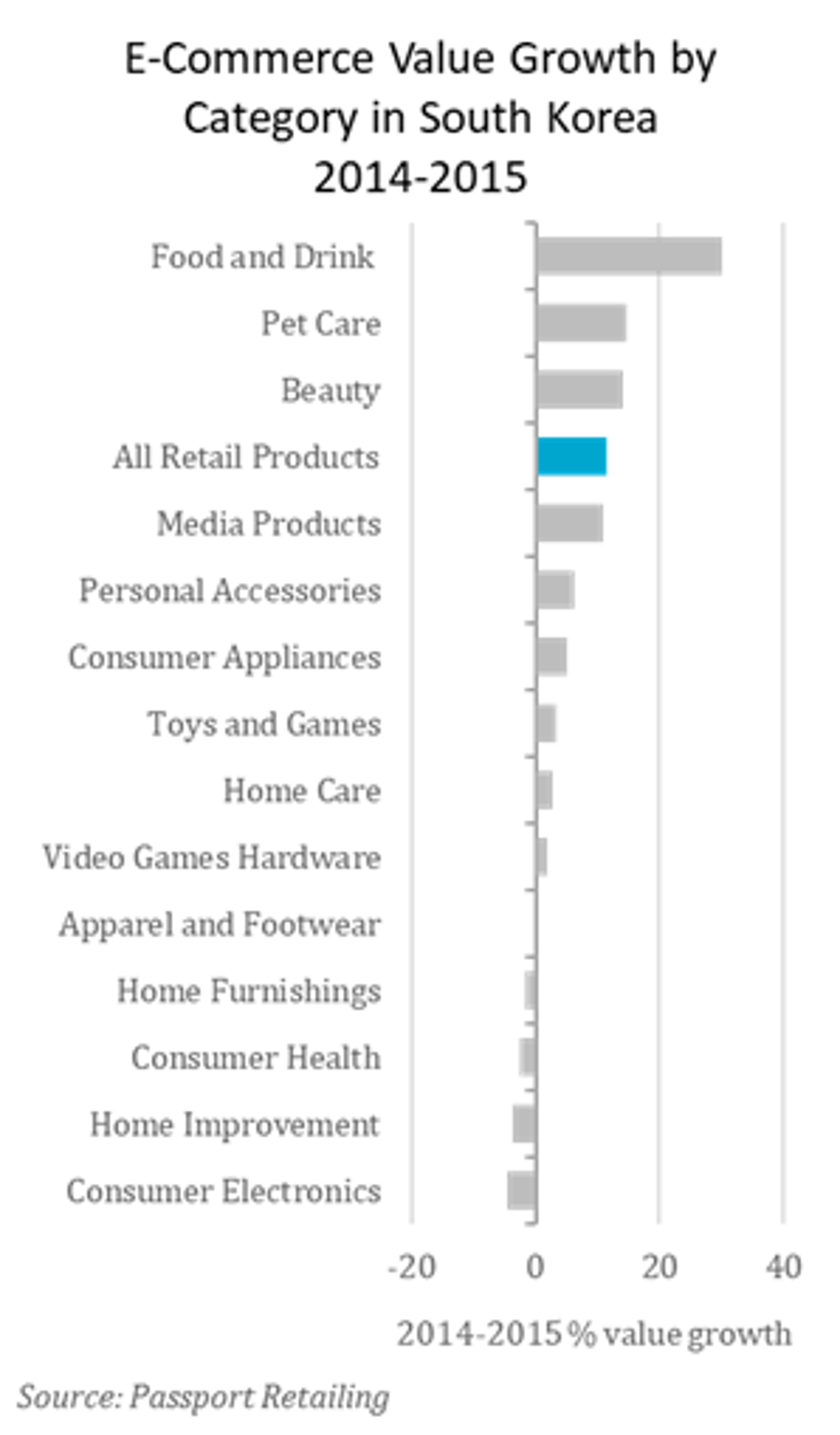
Much like during COVID-19, e-commerce was a bright spot in the South Korean retailing industry during the MERS outbreak. Ordering goods online for delivery proved a safer option. In fact, e-commerce posted double-digital growth in 2015. Food and drink posted 30% sales growth in 2015, more than double the previous year. Buying groceries online was already becoming a regular habit, but fears of infection during the outbreak further propelled its growth, helping South Korea emerge as a posterchild for online grocery retailing globally.
Pet care, beauty and personal care and media products also posted strong e-commerce growth during the outbreak. These categories include products that are necessary to take care of and entertain oneself or animals while at home. E-commerce sales of apparel and footwear, consumer electronics and home furnishings all posted negative growth in 2015 as consumers cut discretionary spend, but all rebounded in 2016.
Lessons from China’s SARS crisis
In November 2002, Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS) emerged in the Guangdong province of southern China but did not spread wide enough to be considered a pandemic. Unlike COVID-19, SARS was generally transmitted after people started showing symptoms, which helped contain the outbreak. Even so, the majority of China was essentially on lockdown in the first half of 2003 as the government tried to minimize disease spread. The country suffered months of economic contraction but rebounded dramatically.
Consumer spending fell as people shunned public places, such as stores and restaurants, to avoid contracting the virus. In China, the retail sector was among the worst hit. Sales growth slowed to 4.3% in nominal terms in May 2003, the slowest monthly growth in 20 years, but bounced back quickly, according to China’s National Bureau of Statistics. The World Health Organization declared that the SARS outbreak had been contained globally in July 2003. By then, retail growth rebounded to pre-crisis levels.
Retailing downturn expected to be more severe than previous crises
The impact of COVID-19 on the retailing industry, and the economy at large, will depend on how long the pandemic lasts and how far it spreads as well as government measures to promote the safety of citizens and prop up the economy.
Growth assumptions were applied to Euromonitor International’s for the U.S. retail industry, in particular, to estimate the potential impact. Assuming a relatively swift recovery, as noted in Euromonitor International’s baseline COVID-19 economic forecast with normalization by Q4 2020, there could be a 6.5% contraction in U.S. retail sales in 2020, resulting in a downgrade of USD221.6 billion from previous baseline estimates. U.S. retail sales contracted by just 2.2% in 2009 in comparison.
There are still several unknowns, including the progression of the virus and government intervention, varying significantly by country. In addition, the digital maturity of some markets may also soften the blow as non-essential stores were closed during lockdowns. However, only 15% of goods were bought online in the U.S. in 2019, compared to 28% in China. Though too many unanswered questions remain to be definitive, these estimates and learnings from past crises provide a sense of the challenges ahead.
