On 11 March 2020, the World Health Organization (WHO) declared the Coronavirus (COVID-19) outbreak, which began in China, a global pandemic. In the last year, and in a world that is more interconnected than ever before, there have been around 115 million global cases recorded and 2.5 million deaths according to Johns Hopkins Coronavirus Resource Center. The pandemic has disrupted consumer markets around the world causing the biggest shock to the global economy since the Great Depression. Governments around the world have been trying to balance lockdowns and social distancing measures to keep populations safe, with the fiscal stimulus to support business and economies, which in turn, have sent government debt levels soaring.
In this context, the way consumers shop, eat, work and play were transformed, changing behaviour and values, often permanently. Euromonitor International's global network of research analysts discuss the economic, consumer and industry landscape one year on with insights including a predicted rebound in consumer expenditure driven by discretionary categories as a result of revenge spending; ongoing business investments to avoid future supply chain shocks; a longer-term shift to the home as the main hub for eating, living and working; and the opportunity to build back better for a more sustainable economic recovery.
Economies
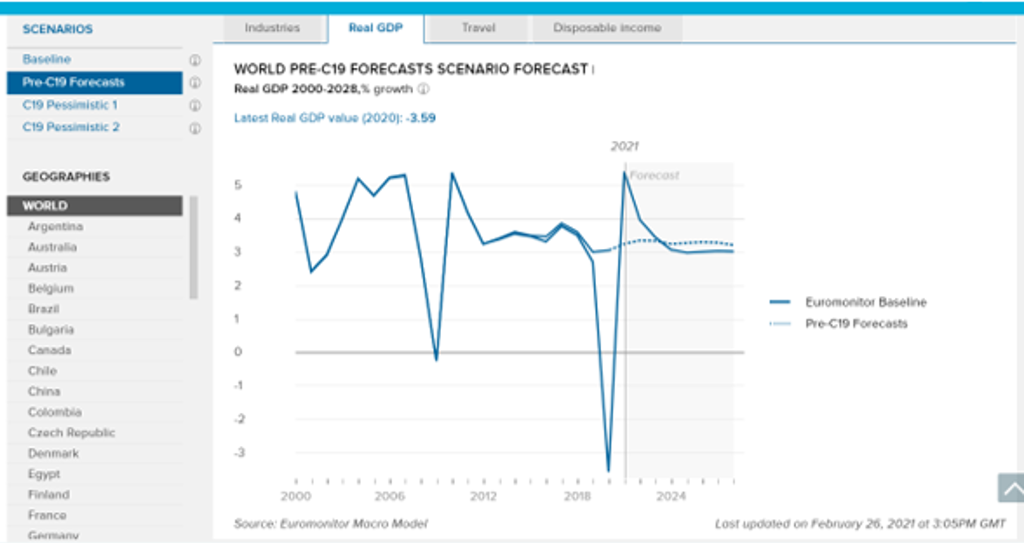
Speed of the global economic recovery uncertain
The global economy contracted by 3.6% in 2020 with a rebound to 5.3% forecast for 2021. Although the global outlook has improved from a year ago, uncertainty remains as to the speed of the recovery, with much faster improvements likely in developed economies, which are leading on vaccine rollouts, compared to developing countries where vaccination will continue into 2022-2023. However, in our worst-case Pessimistic2 COVID-19 scenario, world real GDP would decline by 0-2.0% in 2021, as the spread of more infectious virus mutations leads to more intense and longer-lasting lockdowns and social distancing measures, and sufficient vaccination rates for herd immunity in developed economies are delayed into 2022.
Source: Euromonitor International COVID-19 dashboard
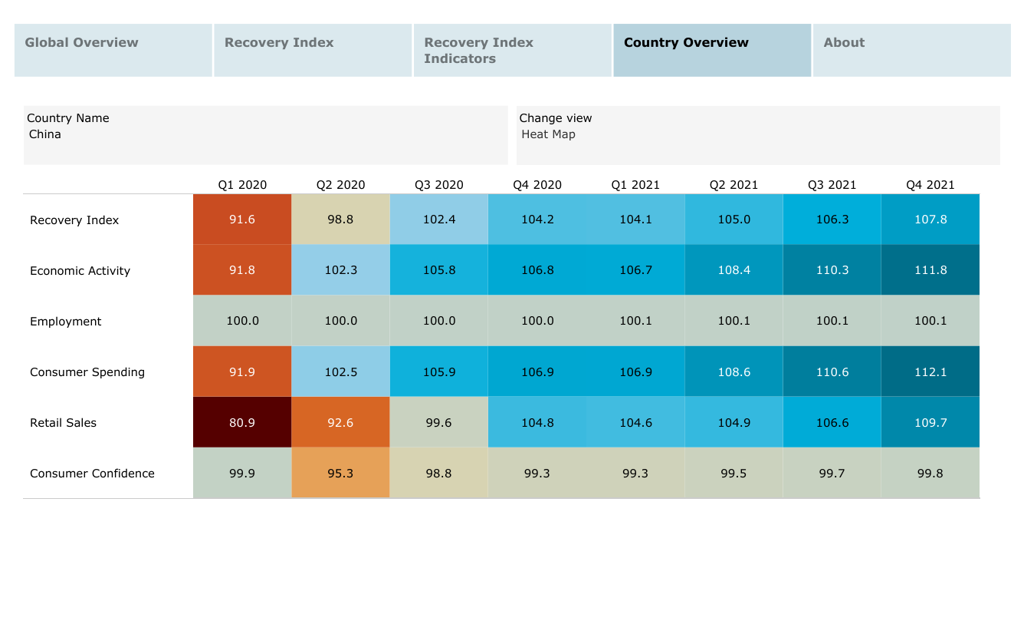
China was the first major economy to return to pre-pandemic levels
Shirley Lu, Research Manager
As new COVID-19 cases in China started to fall from Q2 2020, venues reopened and business activities resumed; China’s economy has since witnessed a robust v-shaped recovery. Euromonitor’s Global Recovery Tracker shows that China was the first major economy to see its real economic output, labour market, and consumer spending return fully to pre-pandemic levels, as of Q3 2020. COVID-19 has left a profound impact on China’s consumer goods and service sectors, disrupting the consumer mindset for hygiene, immunity, and spending behaviour.
Source: Euromonitor International Global Recovery Tracker
Focus on local production and regional alliances in the Middle East
Lois Berman, Head of Middle East and Africa Research
One year on from the outbreak of COVID-19 in the Middle East, a return from lockdown and push on vaccinations means life is returning to normal, though it may not be the same “normal”. While the malls have opened, footfall remains down, with some consumers shifting to purchasing online, mainly due to convenience and the increased availability of apps and websites. Equally, the disruption in the supply chain during the pandemic forced many local and regional players to change strategies towards local production and regional alliances, thereby ensuring ample products and supplies going forward.
Foodservice and travel sectors continue to struggle in Brazil
Angelica Salado, Research Manager Brazil
One year after the confirmation of the first COVID-19 case in Brazil, political instabilities worsened the overall economic prospects for the country. Despite the pessimistic industry expectations in the first semester of 2020, sales of alcoholic drinks, pet care, packaged food, home and garden and consumer electronics continued to grow throughout the year – at the expense of the entertainment, foodservice and travel sectors, that still struggle to overcome long-term social isolation measures.
Consumer Markets
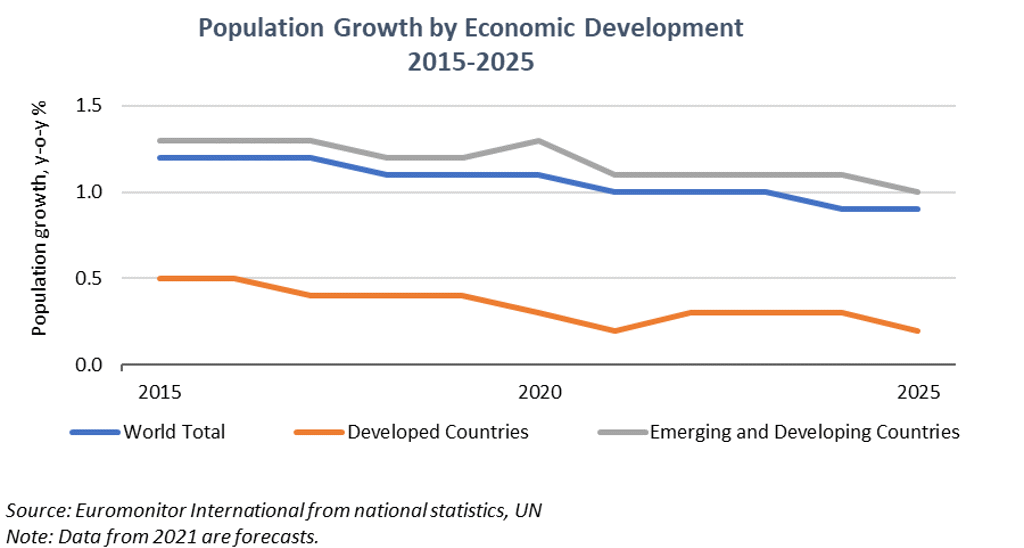
Slower population growth in 2021
Lan Ha, Topic Page Manager, Population
The pandemic has accelerated global demographic challenges, with higher mortality rates, disrupted migration and falling birth rates resulting in slower population growth and changing age structure in many countries. As developed countries’ population is expected to grow by only 0.2% in 2021 (down further from 0.3% in 2020), population ageing will hasten, undermining future consumption and economic growth.
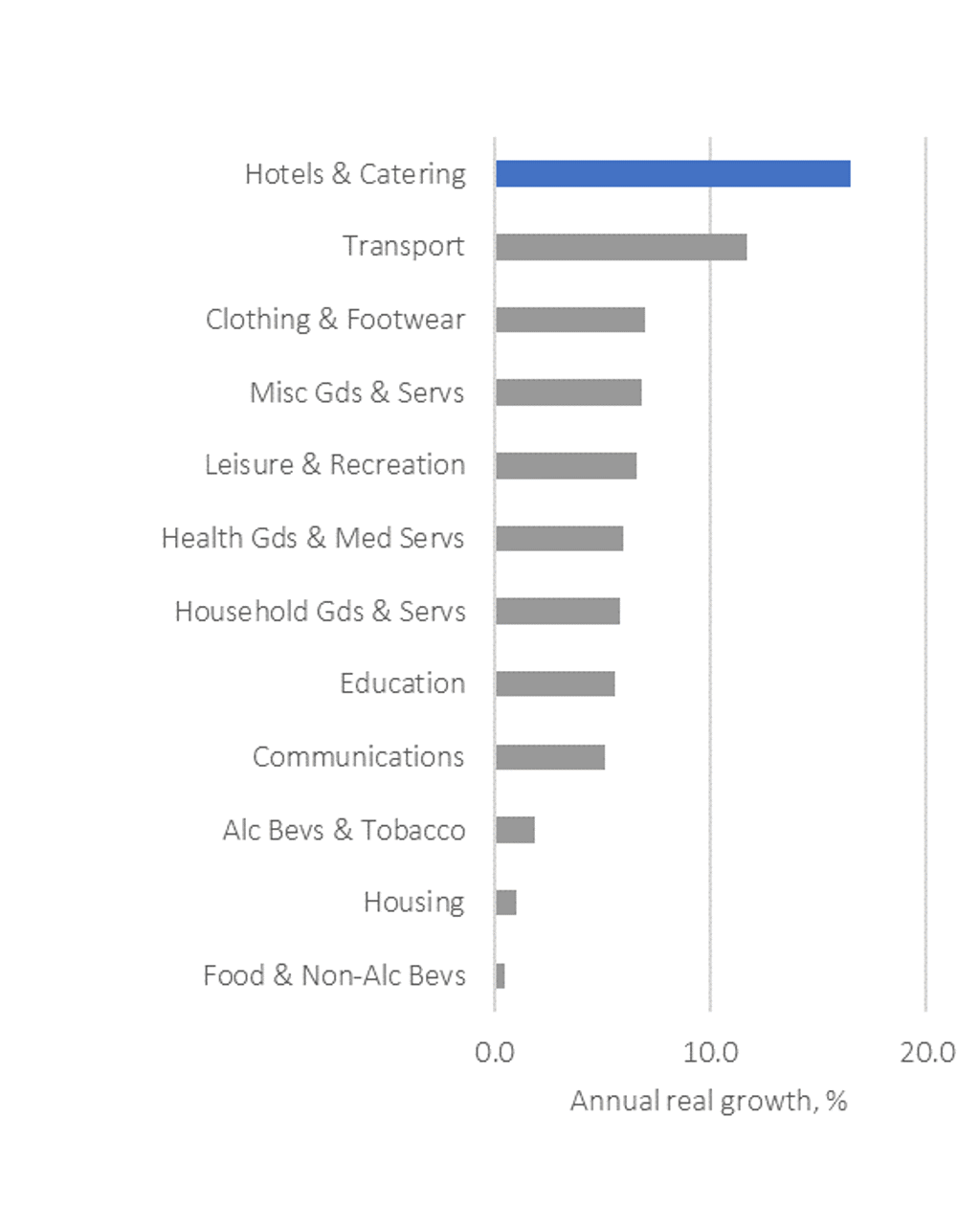
Pent up consumer demand to benefit discretionary expenditure
An Hodgson, Senior Income and Expenditure Manager
Global consumer expenditure fell by 4.9% in real terms in 2020 over a year earlier. Hotels and catering and transport were the two categories that saw the biggest year-on-year declines in 2020, at 17.5% and 14.1% in real terms respectively, as consumers cancelled their holiday plans, dined in, stayed home, and minimised their use of public transport. However, these two categories are expected to record the fastest consumer spending growth in 2021, at 16.5% and 11.7% in real terms respectively, as a result of pent-up demand and global economic recovery.
Global Real Consumer Expenditure Growth by Category 2021
Source: Euromonitor International from national statistics/Eurostat/UNdata/OECD
The (party) lights at the end of the tunnel
Spiros Malandrakis, Industry Manager, Alcoholic Drinks
History might not repeat itself, but it does often rhyme. In alcoholic drinks, as the on-trade continues facing its greatest crisis in over a century, a shift to profitability, higher-margin offerings, avoiding labour-intensive menus and proprietary ingredients, lowering staff members and a nostalgia-infused return to spirit focused classics will be the largely inevitable strategic decisions in the short term.
Nevertheless, in the medium to long term, the pent up demand for indulgence, the increasingly desperate need to socialise again and the pendulum of societal traits shifting back towards hedonism after years of fixation with a clinical approach towards health can lead to a strong bounce back. After all, what followed the great Spanish flu pandemic of 1917 is still known as the Roaring 20s.
E-commerce to drive retail growth to 2025
Michelle Evans, Senior Head of Digital Consumer
The most important retail trend fuelled by COVID-19 was the continued ascension of e-commerce as the digital channel became a lifeline for homebound consumers. Euromonitor estimates that in 2020, products-based e-commerce posted 26% growth in real terms. In a year where few channels grew, e-commerce was the bright spot and is expected to continue on that trajectory. Euromonitor projects that half of the absolute value growth for global retail over the 2020-2025 period will be digital.
Travel industry recovery not expected until 2022
Caroline Bremner, Industry Manager, Travel
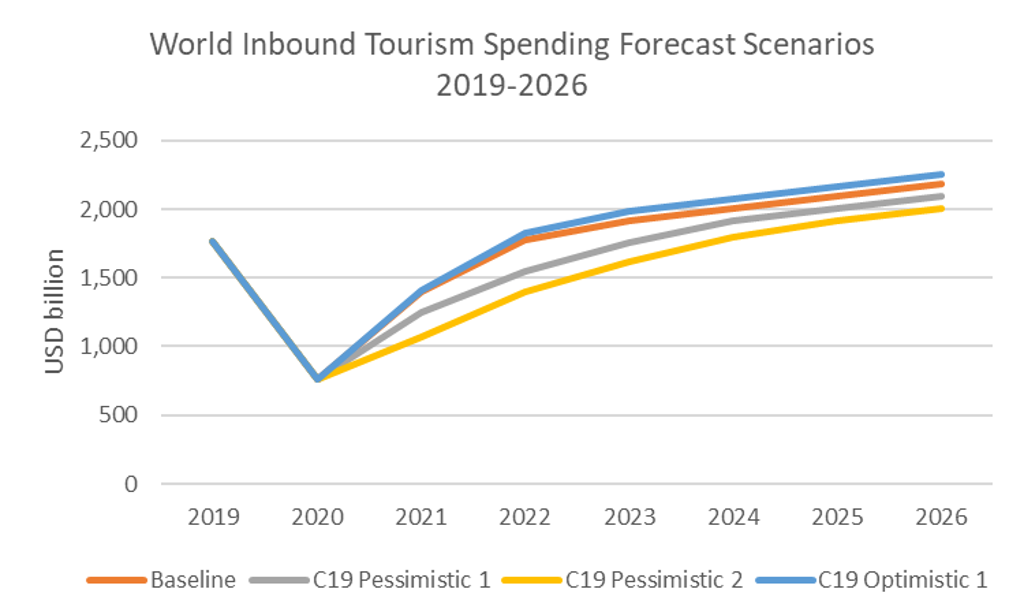
One year on, travel and tourism continue to be beset by the challenges of travel bans and restrictions in many countries, having a devastating impact on travel businesses and local communities. On a global level, inbound tourism spending collapsed by 57% in 2020, and the outlook for 2021 remains highly uncertain, dependent on the speed and scale of mass vaccinations, testing and potential vaccine passports. Recovery to pre-crisis level is expected by 2022 at the earliest and there is a resounding call to build back better and put people and the planet ahead of profit, transitioning to a value-driven tourism model.
Source: Euromonitor International Travel Forecast Model/UNWTO
Eating at home set to remain higher than pre-pandemic levels
Tom Rees, Industry Manager, Food and Nutrition
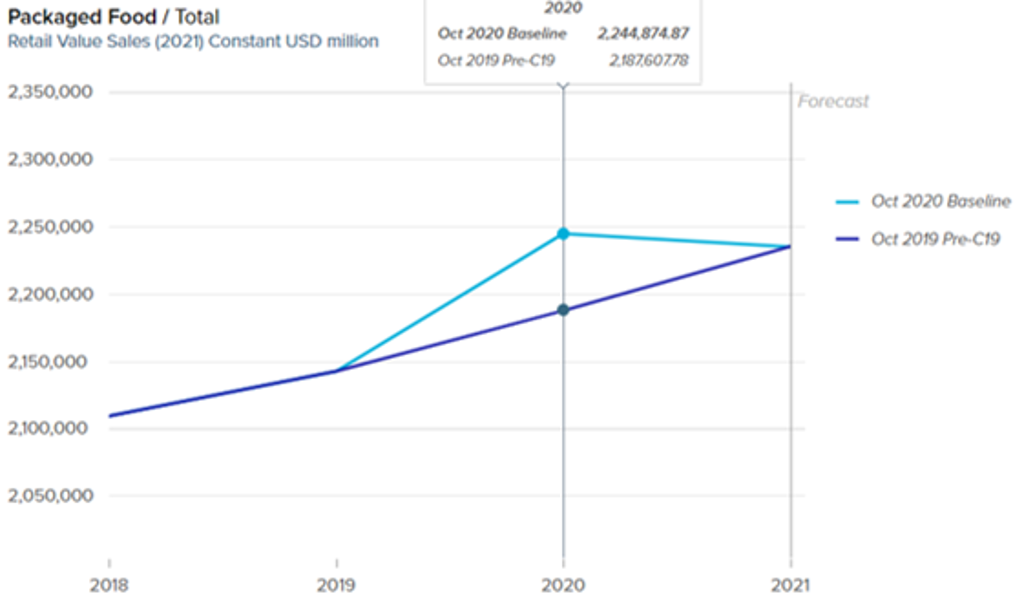
The pandemic’s biggest single impact on packaged and fresh food was the shift in how we ate. As lockdowns went into force across the world, food options such as restaurants, bars, cafés, venues and institutions that served food all closed, increasing the amount consumed in home and consequently how much we needed to buy at retail. Across 2021, this will dissipate somewhat as restrictions on movement and foodservice ease, but retail sales will not simply return to their 2019 level. Uneven vaccine rollouts, varying approaches to easing restrictions on movement and foodservice, residual consumer concern over infection and the economic impact of COVID-19 will all keep home eating higher than it was pre-pandemic.
Business
Investment in supply chains to prevent future shocks
Justinas Liuima, Senior Consultant
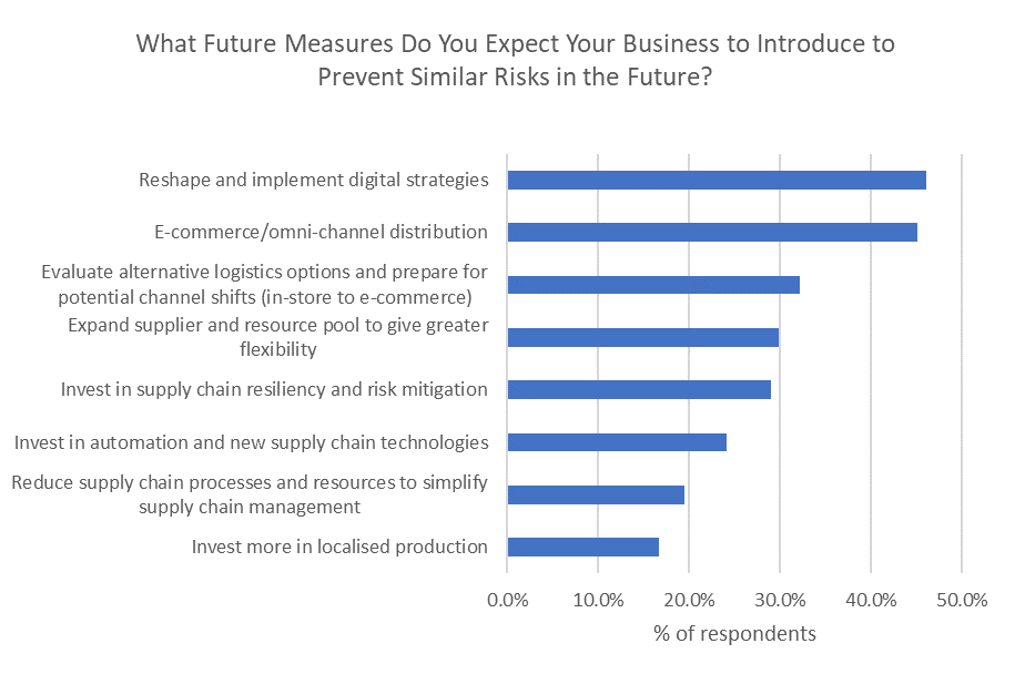
The global manufacturing sector showed swift recovery from the COVID-19 shock and is forecast to grow by 5.3% in real terms in 2021, with hi-tech goods, household goods and pharmaceutical industries showing the fastest growth. Manufacturing companies continue to invest in supply chain localisation, production digitisation and e-commerce to better prepare for similar disruptions in the future.
Source: Euromonitor International Voice of the Industry COVID-19 Survey, October 2020. Note: results show combined responses from Apparel and personal accessories, Automotive, Beauty and personal care, Consumer electronics and appliances, Food and beverages and Household essentials industries; N=1284
Working from home becomes a permanent change
Aiste Kriauciunaite, Survey Analyst
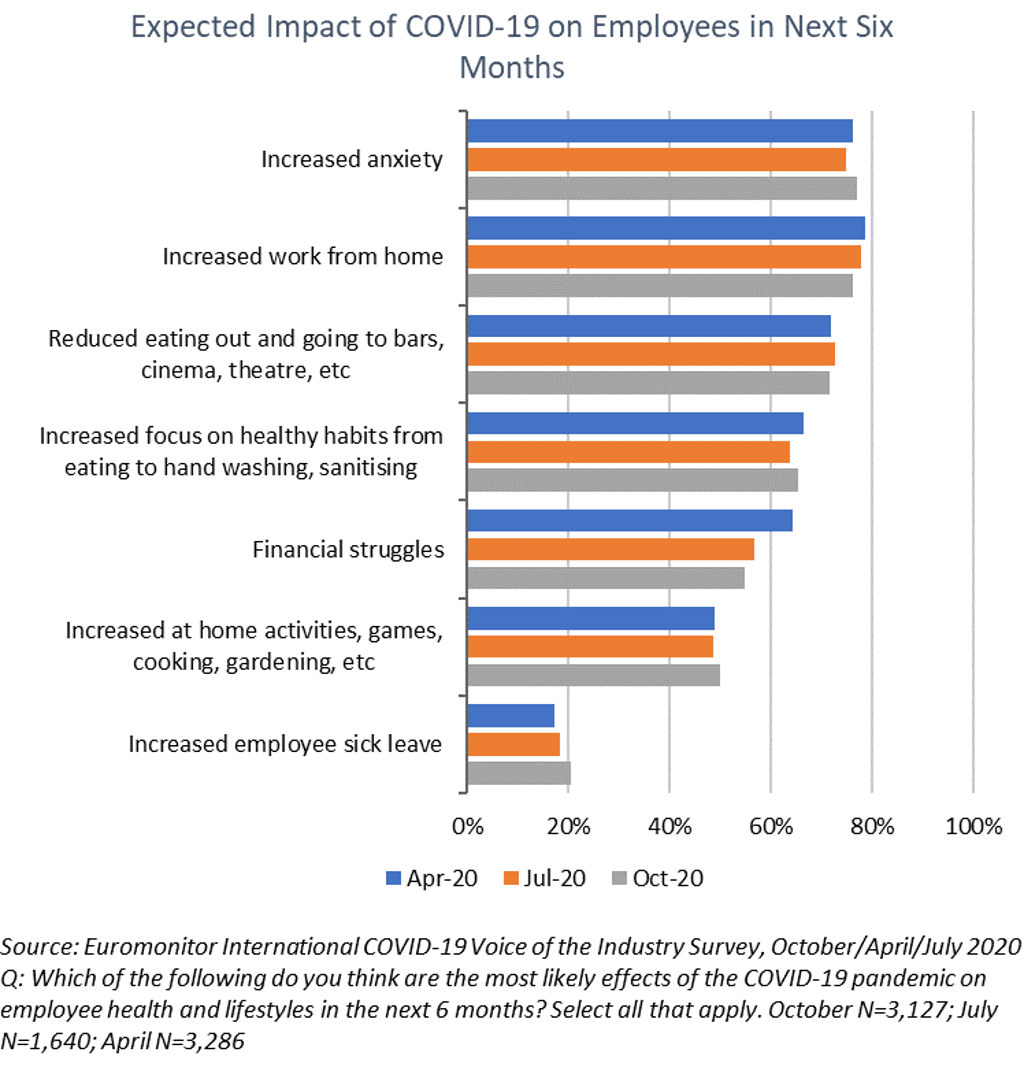
The COVID-19 pandemic has had an extreme impact on business operations worldwide, greatly shifting employee and labour policies in early 2020, with the main precautions taken by companies so far being restricted travel and mandatory working from home. The great majority of companies either created a business continuity plan in response to COVID-19 or are in the process of doing so. Many industries expect that the COVID-19 pandemic will lead to decreased revenue growth in the short term, though the impact is less clear when looking at long-term effects, though most expect working from home to become a permanent feature of life post-COVID-19.
Coronavirus increases polarisation
Zora Milenkovic, Head of Drinks and Tobacco
One year on and the new normal around the world is repeated lockdown cycles, closed borders, medical subjection and digital encroachment. Global employment inactivity has, according to the ILO, increased by 81 million, with the expectation of double-digit growth in business insolvencies across every region by the end of 2021. The gaping chasm between rich and poor, corporates vs independents, self-sovereignty and surveillance has thus resulted in a profoundly politicised and polarised world.
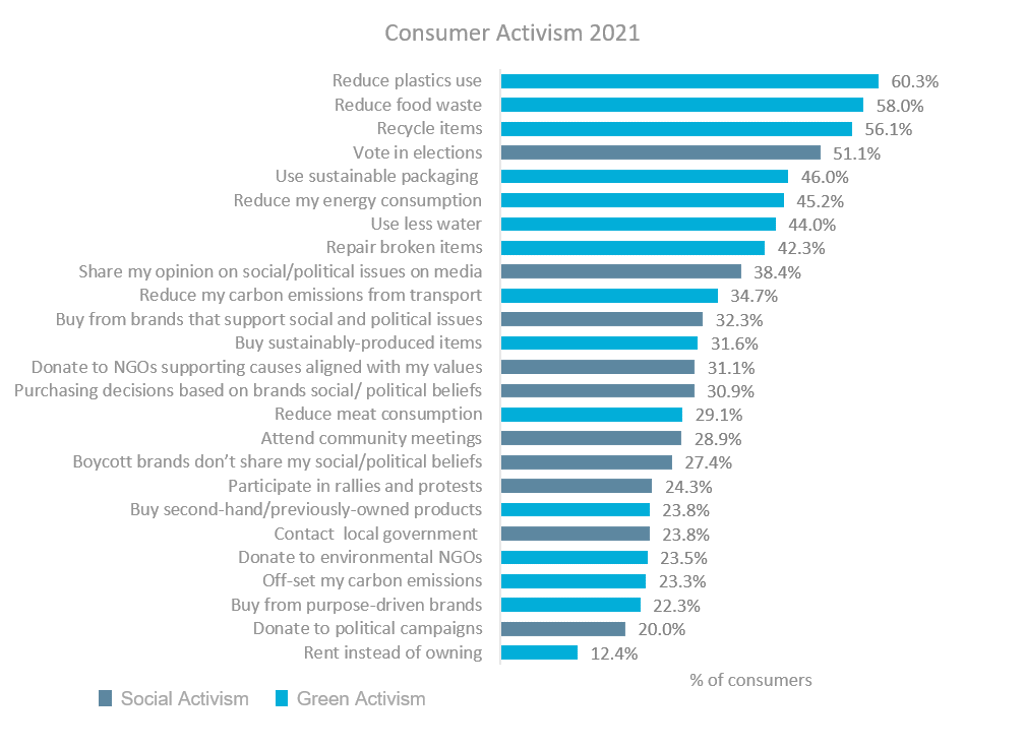
Businesses have a unique opportunity to build back better
Maria Coronado Robles, Topic Page Manager, Sustainability
COVID-19 has been a catalyst for consumer expectations that businesses can do more to tackle global issues and build a better world, with a renewed interest in planetary welfare. Conscious activism is on the rise, with more consumers and brands taking social action. However, the planet remains top of mind, with reducing plastic use, food waste and recycling topping the list of actions for global consumers. Corporate talk is shifting from traditional sustainability messages of “doing less badly” to talk about purpose, responsibility and accountability: “If you are part of the problem, then you must be part of the solution”. It’s not a trend that will fade away, it is the new way of doing business.
Source: Euromonitor International Lifestyles survey, 2021
To stay informed of Euromonitor's latest coronavirus insights, please click here.